Tag: MIT
-

MIT Grieves Shooting Death of Plasma Center Director
MIT Community Mourns a Tragic Loss The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) community is grappling with the sudden and shocking death of a leading figure in plasma science. Officials confirmed that the director of MIT’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center was shot and killed in his home, marking a devastating blow to researchers and colleagues…
-

MIT Grieves: Shooting Death of Plasma Science Center Director
MIT Grieves After Tragic Shooting The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is mourning after the sudden and shocking shooting death of the director of its Plasma Science and Fusion Center. The incident occurred at the director’s home and has left the MIT community grappling with loss, shock, and a renewed focus on campus safety and trust.…
-

MIT Mourns the Loss of Plasma Science Center Director in Tragic Shooting
Overview The MIT community is grieving after the sudden and shocking death of Nuno FG Loureiro, the director of MIT’s renowned plasma science and fusion center. Loureiro, 47, was reportedly shot multiple times at his home, according to university officials. The incident has sent a wave of shock through the campus, where Loureiro is remembered…
-

MIT’s Deep-Learning Model Predicts Fruit Fly Cell Behavior with 90% Accuracy
Overview: A New Window into Early Development Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, led by associate professor Ming Guo, have unveiled a deep-learning model that can predict, minute by minute, how individual cells in a developing fruit fly embryo move, fold, divide, and rearrange. The breakthrough sits at the intersection of biology and artificial…
-
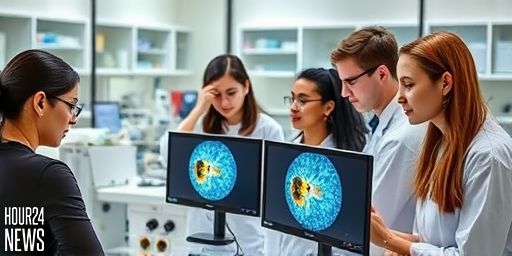
MIT Model Predicts Fruit Fly Cell Behavior with Notable 90% Accuracy
MIT Unveils a Deep-Learning Breakthrough in Embryonic Cell Dynamics Researchers at MIT have developed a deep-learning model that can predict, minute by minute, how individual cells will fold, divide, and rearrange in the earliest stages of a fruit fly embryo. Led by Ming Guo, an associate professor of mechanical engineering, the team’s work marks a…
-

MIT Deep-Learning Model Rearranges Our Understanding of Fruit Fly Cells
MIT Unveils a Deep‑Learning Tool to Predict Fruit Fly Cell Behavior Researchers at MIT, led by associate professor Ming Guo, have developed a cutting‑edge deep‑learning model that forecasts minute‑by‑minute cell actions in fruit fly embryos. The breakthrough promises to illuminate the earliest stages of development and could reshape how scientists study cell mechanics, tissue formation,…
-

Particles that Boost mRNA Delivery Could Lower Vaccine Doses and Costs
New Particle Design Aims to Make mRNA Vaccines More Efficient Scientists at MIT have developed a novel delivery particle that could enhance how mRNA vaccines are presented to the immune system. In preclinical studies, the researchers show that an optimized lipid nanoparticle (LNP) can improve the efficiency with which mRNA is delivered into cells, potentially…
-

MIT Lipid Nanoparticles Boost mRNA Vaccine Efficiency
New Delivery Particles Could Transform mRNA Vaccines A breakthrough from researchers at MIT introduces a novel lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery system designed to improve how mRNA vaccines are delivered inside the body. The team reports that their particles may enhance the effectiveness of mRNA vaccines and enable lower dose requirements, which could in turn reduce…


