Tag: MD Anderson
-
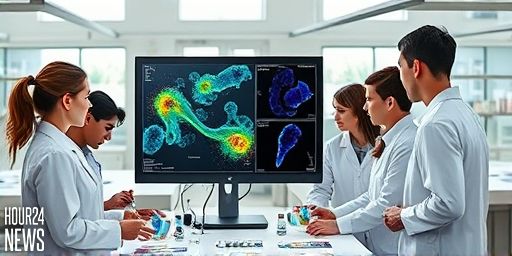
Inflammation Drives Early Lung Cancer: MD Anderson Maps
New Insights into the Onset of Lung Cancer Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have unveiled a landmark approach to understanding how lung cancer begins. By creating high-resolution cellular and molecular maps of lung tissue before and during cancer development, the team shows that chronic inflammation may be a primary driver…
-
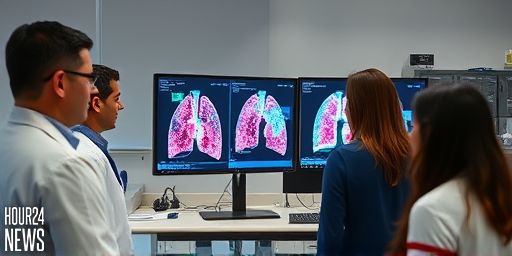
Inflammation identified as a key driver in the earliest stages of lung cancer
New insights point to inflammation as a trigger in early lung cancer Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have unveiled high-resolution cellular and molecular maps that illuminate how inflammation may initiate lung cancer in its earliest stages. The study, which charts the lung’s microenvironment before and during tumor development, suggests that…
-

Inflammation Drives Early Lung Cancer, MD Anderson Study Finds
Overview: Inflammation as an Early Driver of Lung Cancer A groundbreaking study by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center suggests that inflammation may be a crucial catalyst in the very first stages of lung cancer development. By assembling high-resolution cellular and molecular maps of lung tissue before and during tumor emergence,…
-

Cancer-Related Nerve Injury: A Barrier to Effective Immunotherapy
Cancer has always presented formidable challenges in treatment, but new research highlights a lesser-known complication: cancer-related nerve injury. This groundbreaking work from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center reveals how cancer cells can damage the protective covers around nerves, leading to chronic inflammation that ultimately results in immune exhaustion and resistance to immunotherapy.…
