Tag: inflammation
-
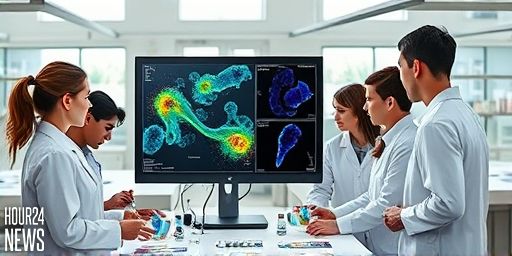
Inflammation Drives Early Lung Cancer: MD Anderson Maps
New Insights into the Onset of Lung Cancer Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have unveiled a landmark approach to understanding how lung cancer begins. By creating high-resolution cellular and molecular maps of lung tissue before and during cancer development, the team shows that chronic inflammation may be a primary driver…
-
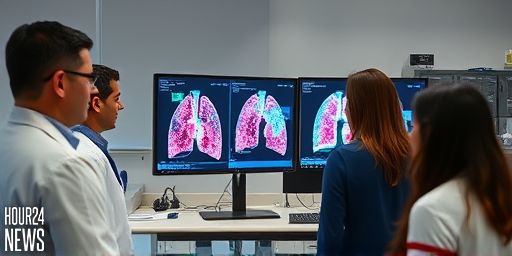
Inflammation identified as a key driver in the earliest stages of lung cancer
New insights point to inflammation as a trigger in early lung cancer Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have unveiled high-resolution cellular and molecular maps that illuminate how inflammation may initiate lung cancer in its earliest stages. The study, which charts the lung’s microenvironment before and during tumor development, suggests that…
-

Inflammation Drives Early Lung Cancer, MD Anderson Study Finds
Overview: Inflammation as an Early Driver of Lung Cancer A groundbreaking study by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center suggests that inflammation may be a crucial catalyst in the very first stages of lung cancer development. By assembling high-resolution cellular and molecular maps of lung tissue before and during tumor emergence,…
-

Lauric Acid and Levodopa Mitigate Manganese-Induced Ovarian Toxicity in Mice Through Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Steroidogenic Pathways
Overview Manganese, a naturally occurring element, can exert toxic effects on the female reproductive system at high exposure levels. Recent experimental work in BALB/c mice explored whether two compounds, lauric acid and levodopa, individually or together, can attenuate manganese-induced ovarian toxicity. The study centers on antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and steroidogenic pathways as key mediators of protection.…
-

Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria and Heart Health: What the New Study Reveals
Overview: CSU and Cardiovascular Risk Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is more than a skin condition. Recent research has highlighted a potential link between CSU and an elevated risk of several cardiovascular diseases. While CSU is primarily characterized by recurrent hives and itching lasting six weeks or longer, the inflammatory processes behind CSU may extend beyond…
-

Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria Linked to Increased Heart Disease Risk: What It Means for Patients
Overview: CSU and cardiovascular risk Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), a condition characterized by persistent hives and itching with no identifiable trigger, affects a significant portion of adults worldwide. Recent research has begun to shed light on a potential link between CSU and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). While CSU is primarily a dermatologic…
-

HPO Axis & Brain Aging: Ovarian Disorders & Neurodegeneration
Understanding the HPO Axis in Female Health The hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis is a finely tuned endocrine feedback loop that governs ovulation and reproductive function in female vertebrates. Proper balance relies on the regulated secretion of sex steroids by the ovarian follicle to inhibit pulsatile release of gonadotropins from the pituitary. Disruptions in any component of…
-

HPO Axis and Brain Aging: Ovarian Disorders Explained
Introduction: Connecting the HPO Axis to Brain Aging The hypothalamic‑pituitary‑ovarian (HPO) axis sits at the center of female reproductive health, orchestrating ovulation through a delicate balance of hormones. Recent reviews highlight how disruptions in this axis not only drive ovarian disorders such as menopause, primary ovarian insufficiency (POI), and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) but may…
-

The HPO Axis, Ovarian Disorders, and Brain Aging: Connecting Reproductive Health to Neurodegeneration
Understanding the HPO Axis and Its Role in Reproductive Health The hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis is a finely tuned endocrine system that governs female reproduction. It starts in the hypothalamus, where gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) prompts the pituitary to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones, in turn, regulate ovarian follicle development and the…

