Tag: E. coli
-

Court condemns eThekwini for unlawful beach reopenings amid E. coli risks
Judgment frames a strong rebuke to eThekwini Municipality The KwaZulu-Natal High Court has issued a scathing ruling against the eThekwini Municipality, accusing it of endangering public health by reopening beaches with dangerously high levels of E. coli without provincial authorization. The case centers on whether the city acted within the law when it allowed beach…
-

Court Slams eThekwini Municipality Over unlawful beach reopenings amid E. coli risks
Overview of the Judgment The KwaZulu-Natal High Court has delivered a decisive ruling against the eThekwini Municipality, accusing the city of endangering residents by reopening beaches that showed dangerously high levels of E. coli. The case highlights severe concerns about public health governance and the proper channel for provincial authorization before public-facing amenities like beaches…
-

Court slams eThekwini over unlawful beach reopenings
Coastal health at stake: what the ruling says The KwaZulu-Natal High Court has delivered a scathing judgment against the eThekwini Municipality, accusing it of compromising public health by reopening beaches despite dangerously high E. coli levels. The ruling underscores that provincial authorities did not grant the necessary approvals before these reopenings, turning a local beach…
-

Advanced disease modeling shows some gut bacteria can spread as rapidly as viruses
New findings: gut bacteria spreading like viruses? A new wave of advanced disease modeling points to an unsettling possibility: certain gut bacteria may disseminate through populations as rapidly as some respiratory viruses. In particular, the study highlights Escherichia coli (E. coli) as a bacterium that could exhibit swifter spread than previously imagined under real-world conditions.…
-
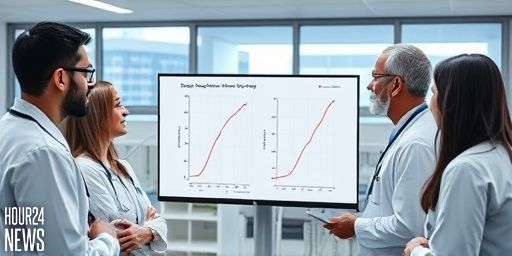
How Some Gut Bacteria Like E. coli Can Spread as Fast as Viruses, New Modeling Suggests
Introduction: A Surprising Parallel Between Bacteria and Viruses In a groundbreaking line of research, scientists have used advanced disease modeling to explore how certain gut bacteria might spread through populations with speeds previously thought possible only for viruses. The focus is on Escherichia coli (E. coli), a common inhabitant of the human gut, and the…
-

Advanced modeling shows some gut bacteria can spread as rapidly as viruses
New insights from advanced disease modeling In a surprising development, researchers using advanced disease modeling have suggested that certain gut bacteria could spread through populations at rates comparable to some viral infections. The focus is on Escherichia coli (E. coli), a common inhabitant of the human gut whose behavior under stress or unusual conditions may…
-

Study Links Nearly 1 in 5 UTIs to Contaminated Meat: A Food-Safety Wake-Up Call
Overview: A New Angle on Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue, typically treated as a medical and hygiene concern. A four-year study, published in mBio, reframes UTIs as partly a food-safety issue by linking about 18% of infections to E. coli strains that originate in meat from food-producing animals.…
-

Study Links Nearly 1 in 5 UTIs to Contaminated Meat
New findings reposition UTIs as a food safety issue A four-year study conducted in Southern California reveals that nearly one in five urinary tract infections (UTIs) may be caused by E. coli bacteria transmitted through contaminated meat. Published in the journal mBio, the research analyzed thousands of samples from UTI patients and retail meat to…
-

Study Links Nearly 1 in 5 UTIs to Contaminated Meat, Reframing a Common Infection as a Food Safety Issue
Groundbreaking findings connect urinary tract infections to contaminated meat A four-year study published in mBio suggests that nearly one in five urinary tract infections (UTIs) may be linked to E. coli bacteria transmitted through contaminated meat. By analyzing more than 5,700 bacterial samples from UTI patients and retail meat in Southern California between 2017 and…
-

Could Martian Ice Preserve Clues of Ancient Life in a Frozen Time Capsule
A Potential Time Capsule Beneath Mars’ Ice Planetary scientists may have found a natural time capsule on Mars. A new study from NASA and Penn State University argues that fragments of biomolecules from ancient microbes could survive long enough in Martian ice to be detectable by future missions. If correct, this means life’s signature —…
